blog post
More than one third of Thais are overweight and one tenth are obese.
According to the 2009 Thai Health Survey, 16 million Thais are obese, with 4.7 million men and 11.3 million women obese.
The obesity situation in Thailand has been on the rising trend of continuously. In 2009, it was found that more than 1 in 3 Thais over 15 years of age and over were overweight (BMI 25 kg/m2 and over) and 1 in 10 were obese (BMI 30 kg/m2 and over).
Compared to other countries in the region, Thais are the second most obese population in
Source: https://www.healthworks.my/malaysians-most-obese/
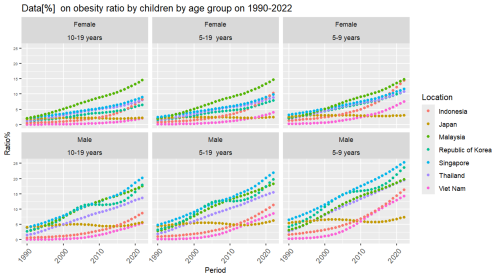
The 2009 survey reveals how around one tenth of Thai pre-school (1-5 years) and school (6-14 years) children were overweight or obese.
Obesity problems in Thailand are continuously increasing. The main causes are inappropriate eating behaviors and sedentary lifestyles. Obesity not only has long-term negative health effects such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease, but also affects the country's economy.
Source: WHO, prepared by HS-TECH Engineering
(Fern)
1 ใน 3 ของประชากรไทยเป็นโรคอ้วน และ 1 ใน 10 มีภาวะอ้วน
จากการสำรวจสุขภาพคนไทยปี 2552 ปรากฎว่าคนไทยอ้วนลงพุงรวม 16 ล้านคน พบผู้ชายอ้วน 4.7 ล้านคน ผู้หญิงอ้วน 11.3 ล้านคน
สถานการณ์โรคอ้วนในประเทศไทยมีแนวโน้มเพิ่มสูงขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยในปี 2552 พบว่าคนไทยอายุ 15 ปีขึ้นไป มากกว่า 1 ใน 3 มีภาวะน้ำหนักเกิน (BMI ตั้งแต่ 25 กก./ตร.ม. ขึ้นไป) และ 1 ใน 10 มีภาวะอ้วน (BMI ตั้งแต่ 30 กก./ตร.ม. ขึ้นไป).
หากเปรียบเทียบในระดับภูมิภาค คนไทยอ้วนมากเป็นอันดับ 2 ใน 10 ประเทศอาเซียน รองจากมาเลเซีย ซึ่งหากแยกดูตามเพศชายไทยอ้วนเป็น
Source: https://www.healthworks.my/malaysians-most-obese/
อันดับที่ 4 ขณะที่หญิงไทยอ้วนเป็นอันดับที่ 2 ที่น่ากังวลคือ สถานการณ์เด็กอ้วนที่มีแนวโน้มเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างชัดเจนเช่นกัน จากการสำรวจในปี 2552 เด็กไทยปฐมวัย (อายุ 1-5 ปี) และวัยเรียน (อายุ 6-14 ปี) ประมาณ 1 ใน 10 คนมีภาวน้ำหนักเกินและอ้วน.
ปัญหาโรคอ้วนในประเทศไทยกำลังเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยมีสาเหตุหลักมาจากพฤติกรรมการบริโภคที่ไม่เหมาะสมและการใช้ชีวิตที่ขาดการเคลื่อนไหว โรคอ้วนไม่เพียงแต่ส่งผลเสียต่อสุขภาพในระยะยาว เช่น โรคเบาหวาน โรคความดันโลหิตสูง และโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือดเท่านั้น แต่ยังส่งผลกระทบต่อเศรษฐกิจของประเทศด้วย.
Source: WHO
(Fern)